Monday, February 7, 2011
Wednesday, February 2, 2011
6.9 Signal Restoration, Gain and Nonlinearity
- Logic devices must incorporate both gain and nonlinearity to provide nonzero noise margins
- Logic devices must demonstrate a gain greater than unity when transition from VIL to VIH
- Signal Restoration and Nonlinearity
Monday, January 31, 2011
Thursday, January 27, 2011
6.7 Physical Structures of MOSFET
- The on-resistance of MOSFET depends on its physical properties (ie. geometry)
- Silicon doped with material rich in electrons is called n-type semiconductor (n+)
- Silicon doped with material rich in holes is called p-type semiconductor (p+)
- Ron is the resistance of n channel
- Rn is resistance per square of n channel MOSFET in on state.
- Ron = (Rn*L)/W
- In VLSI technology, there is min fabricatable value for MOSFET channel length

Wednesday, January 26, 2011
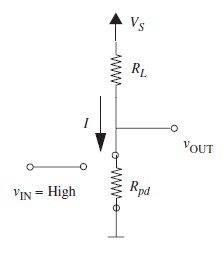
SR Model of MOSFET
- S model is a gross simplification of MOSFET
- A practical MOSFET displays a non-zero resistance between its D and S terminals when it is on
- A more accurate model of MOSFET uses resistance Ron between D & S.


- SR model is still a gross simplification of MOSFET behavior.( Ron is not fixed but a function of VGS)
- Fixed resistance model is simpler and suffices for analyzing some aspect of digital circuit because the gate voltage is bimodal.
- SR model is valild only when VDS <= VGS - VT and when there is only one value for gate voltage when input is high ( VGS = VS)
Tuesday, January 25, 2011
Monday, January 24, 2011
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)